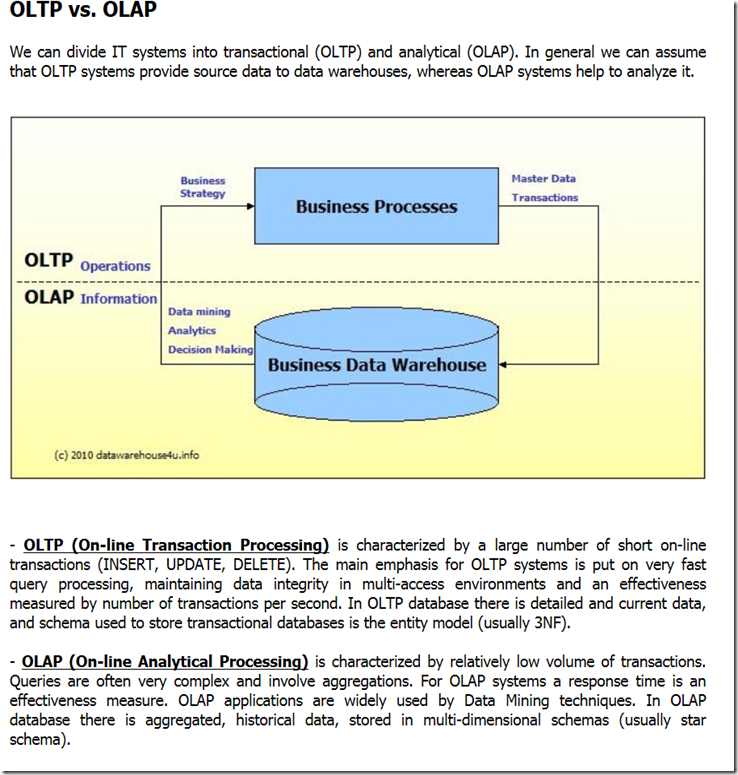
Introduction to SQL Server
SQL Server Management Studio
Delete a DB
Add a DB
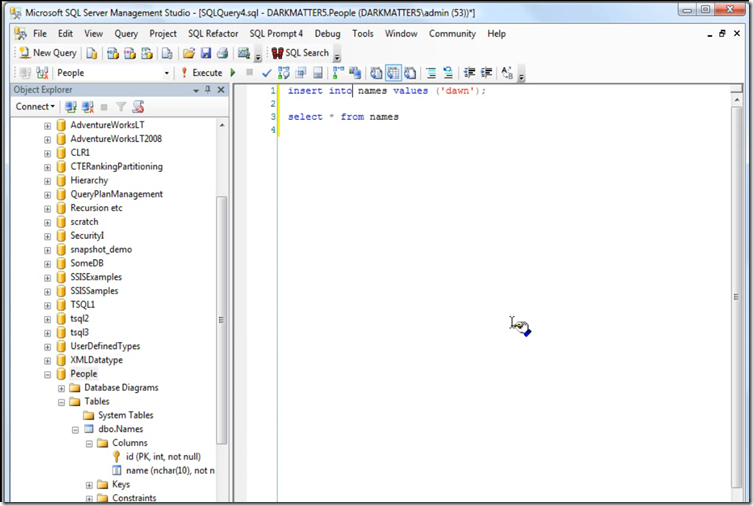
Using T-SQL via GUI
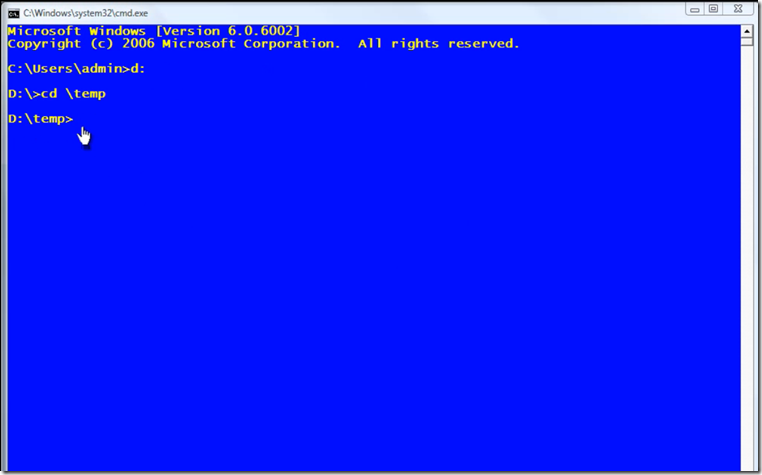
Using SQLCMD in Command Window
Using SQLPS (POWER SHELL) in Command Window
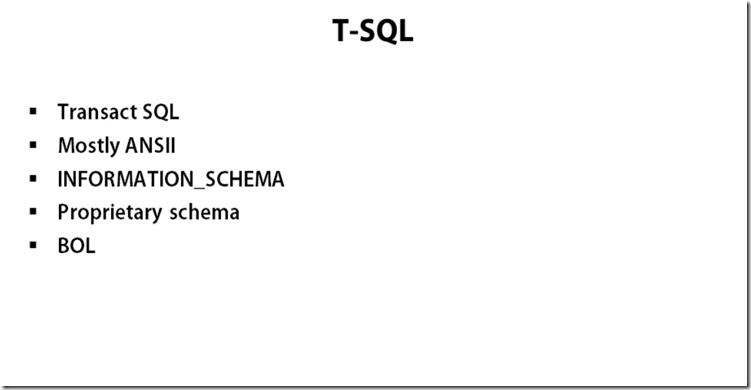
Using T-SQL
SQL Server Meta Data
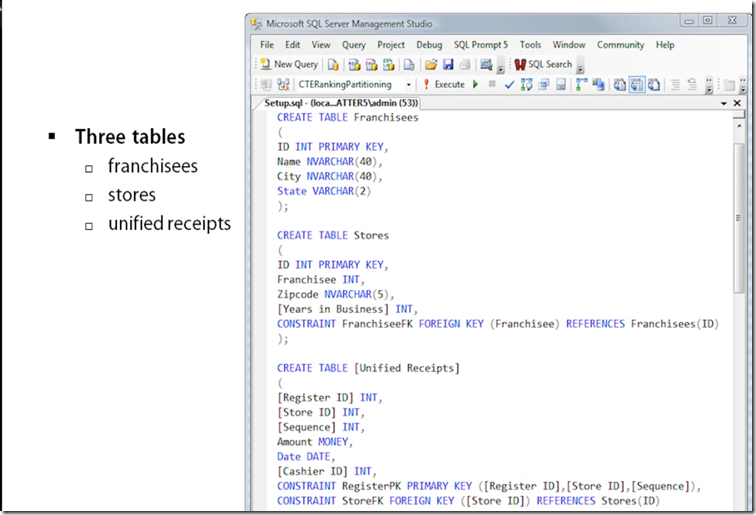
T-SQL Example
Scripting Objects
LINQ To SQL
SQL Server Management objects
Analysis and Reporting
SQL Server Analysis Services and Multi Dimensional Expressions
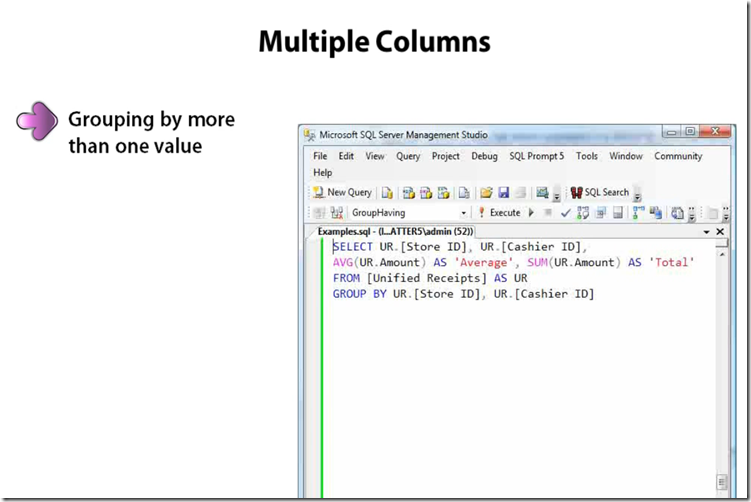
Using Group By and Having
CTE's and Ranking
Same can be achieved in Temporary Table concepts
Same can be achieved in Below Sub Query style
Demo of CTE
Delete large table in Batch by Batch
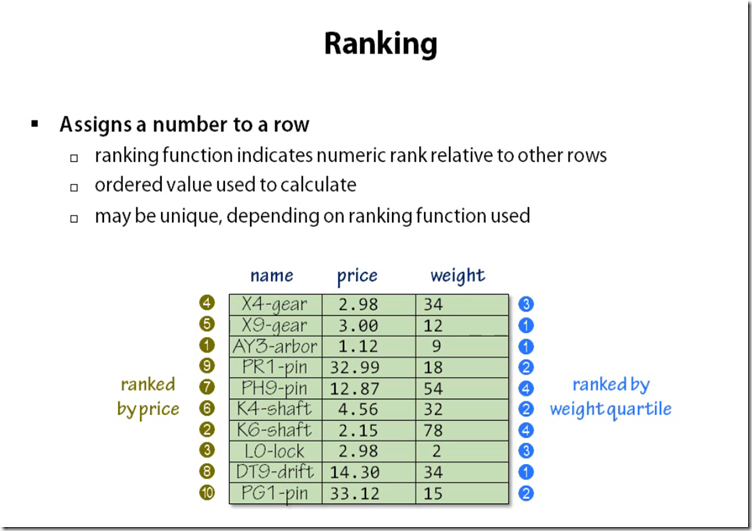
Ranking Functions
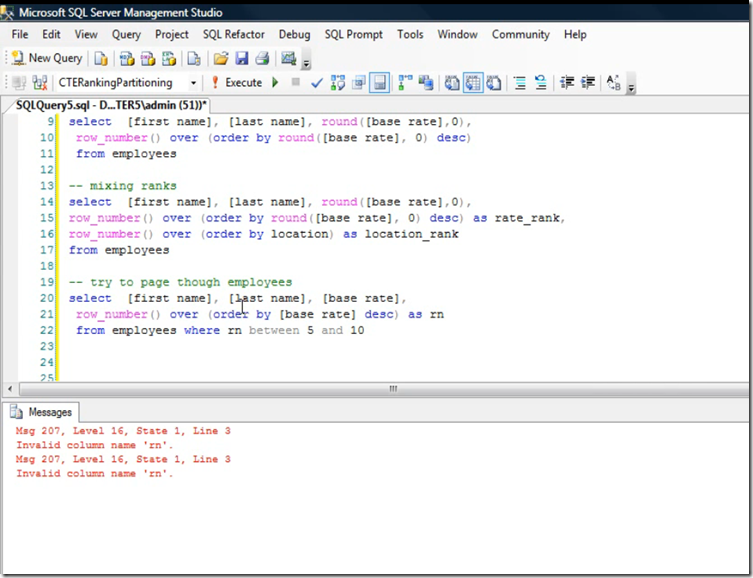
Demo of Row Number
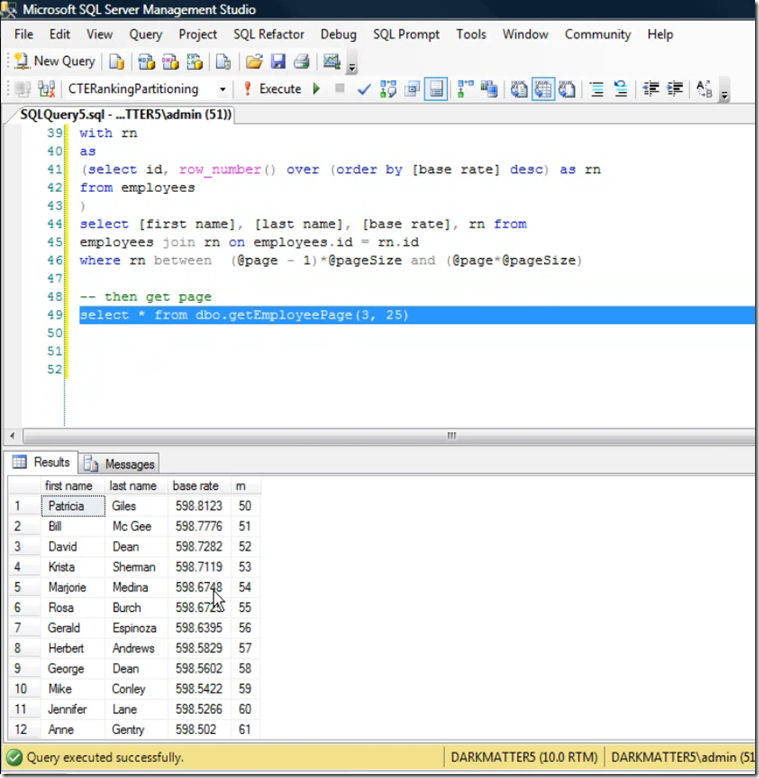
Mixing multiple rankings and CTE with Ranking function to paging through employees
Paging with Table Valued function
Demo of RANK and DENSE RANK
Demo of NTile
Partitioning feature in Ranking function
There are physical partitioning in file, indexes and some other things. Here we are talking about logical partitioning…..
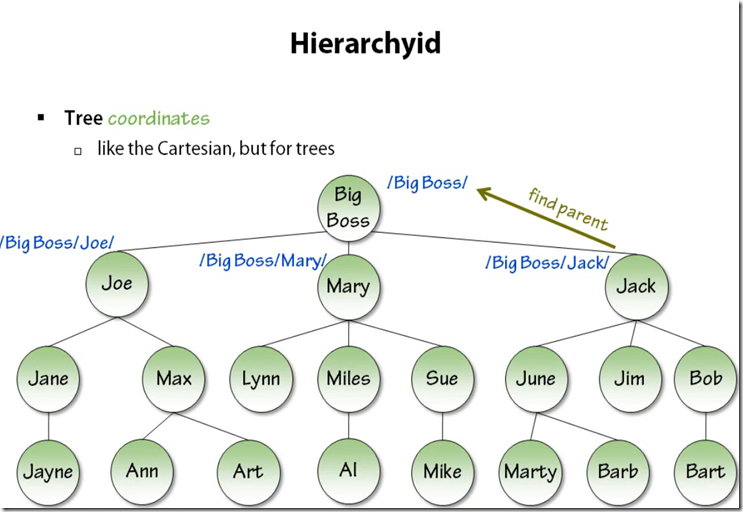
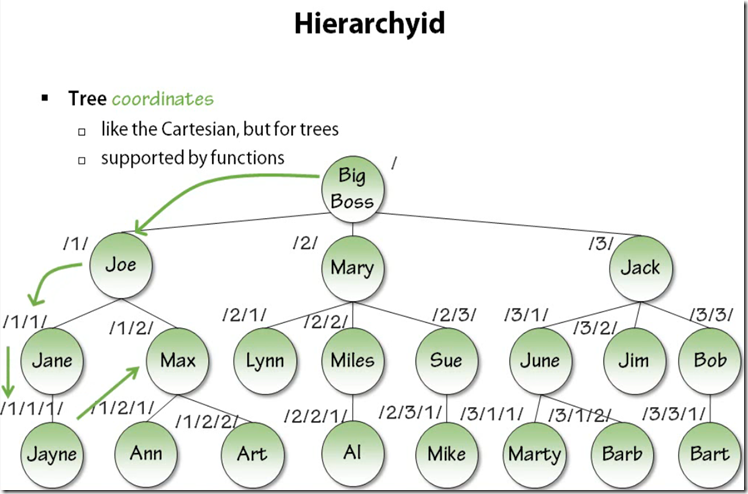
Hierarchies
Basic Properties of Hierarchy id
Demo of Hierarchy ID with Table Representation
Manually Find the Descendants
Demo of IsDescendantsOf
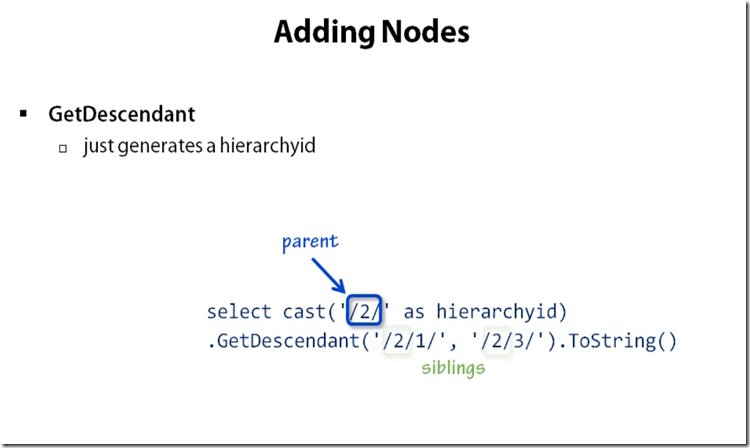
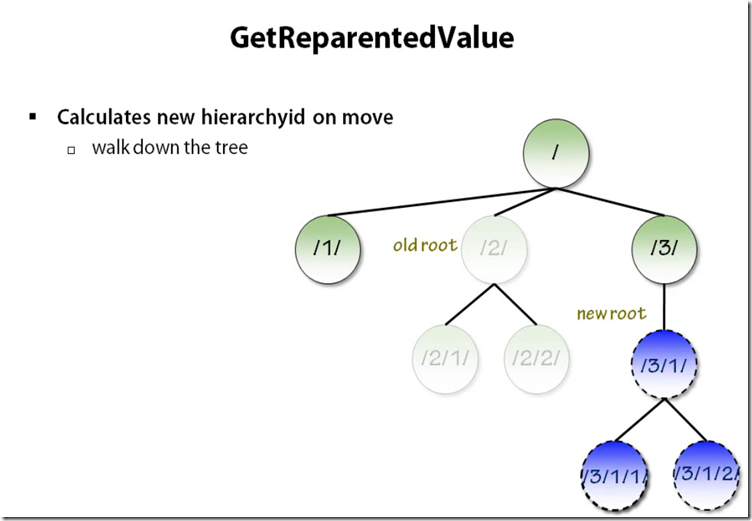
Adding Nodes in Tree
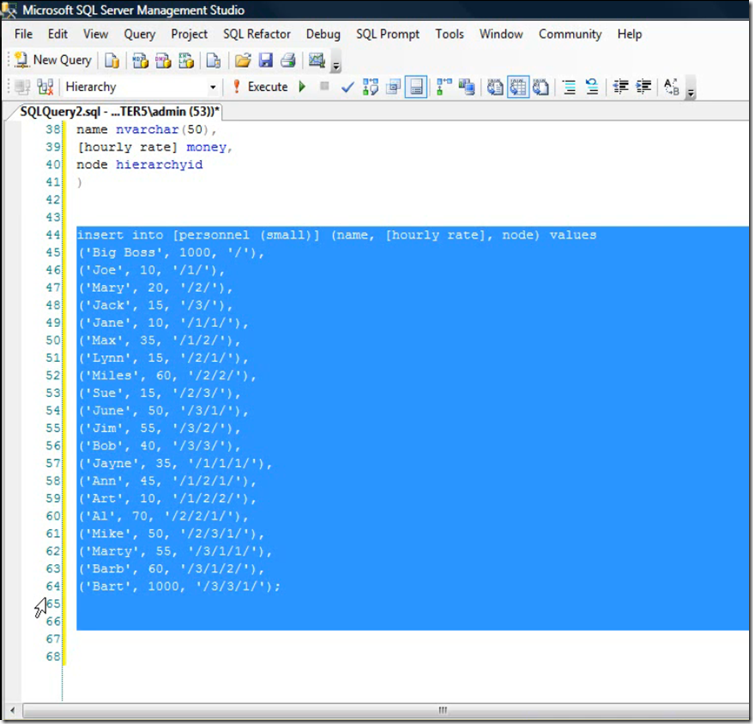
Demo to Add New Node
Adding Nodes Before and After
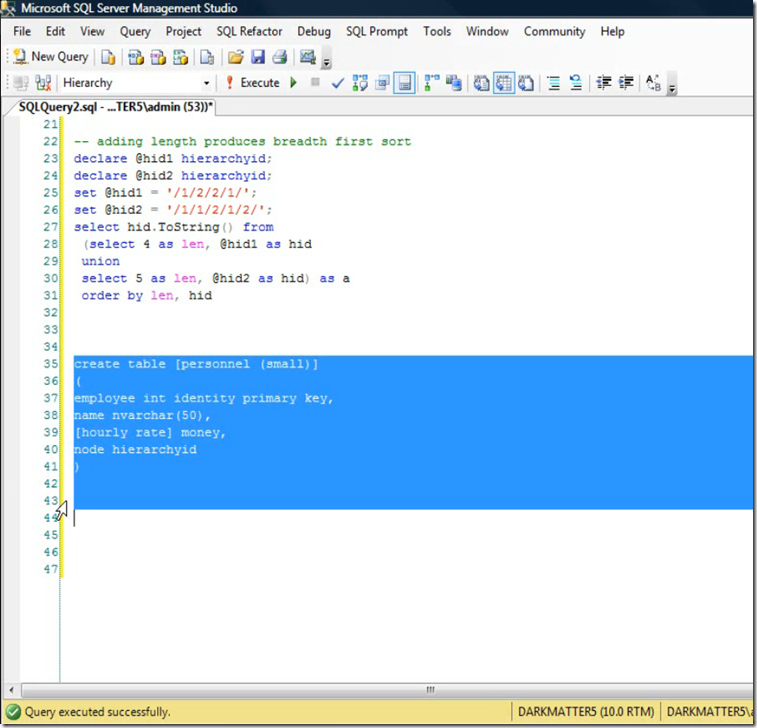
Incrementally Adding Hierarchy id to table
Depth First Search
Depth-first search (DFS) is an algorithm for traversing or searching tree or graph data structures. One starts at the root (selecting some node as the root in the graph case) and explores as far as possible along each branch before backtracking.
Breadth First Search
In graph theory, breadth-first search (BFS) is a strategy for searching in a graph when search is limited to essentially two operations: (a) visit and inspect a node of a graph; (b) gain access to visit the nodes that neighbor the currently visited node. The BFS begins at a root node and inspects all the neighboring nodes. Then for each of those neighbor nodes in turn, it inspects their neighbor nodes which were unvisited, and so on.
Recursion, Pivoting, and Sampling
Demo of Recursion
Tabular Recursion Example
Pivot and UnPivot representation
Cross Tab example
Cross Tab with out Pivot option
Note: Pivot is operator which will perform operation on Table on SELECT clause directly. Also, SELECT Clause will pick up the column from Pivot result.
UnPivot
Initial Stage before Pivot
Unpivot operation without UnPivot operator
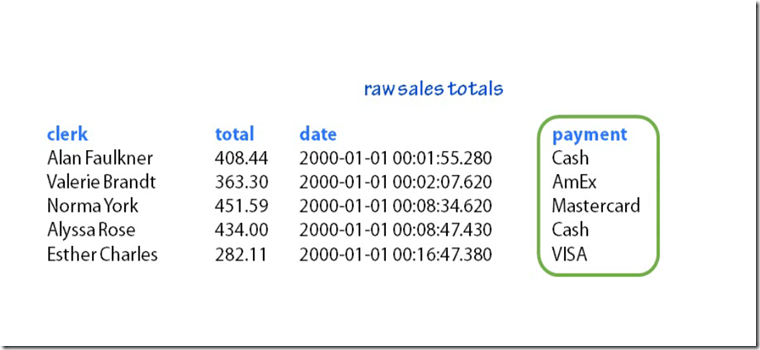
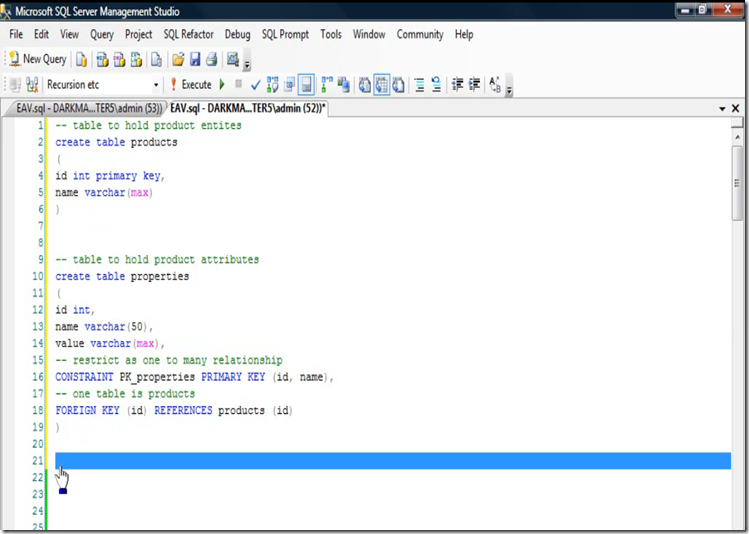
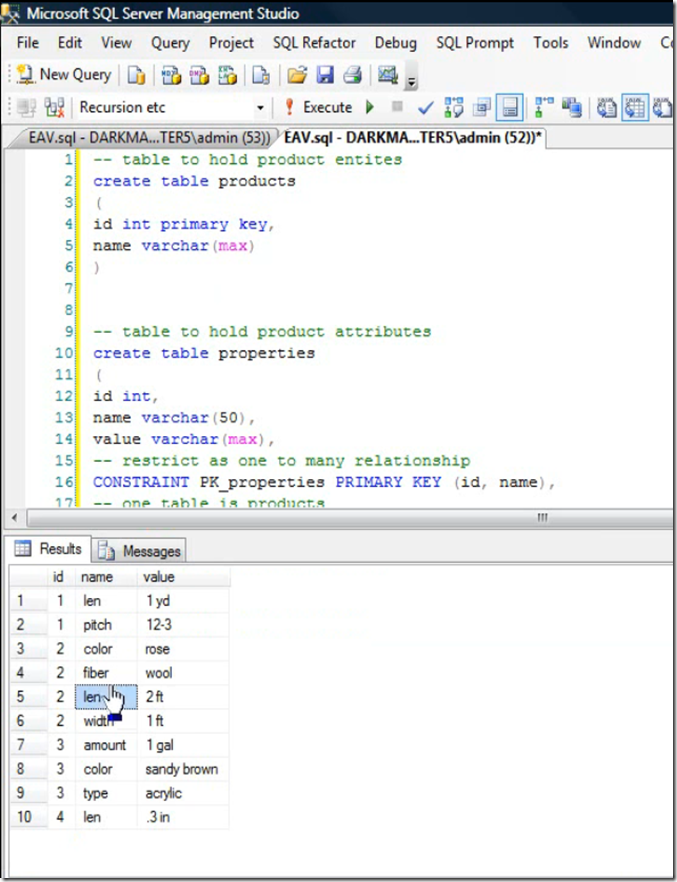
Example of Entity Attribute table
Sampling
Example of Random row selection
CHECKSUM computes a hash value, called the checksum, over its list of arguments. The hash value is intended for use in building hash indexes. If the arguments to CHECKSUM are columns, and an index is built over the computed CHECKSUM value, the result is a hash index. This can be used for equality searches over the columns.
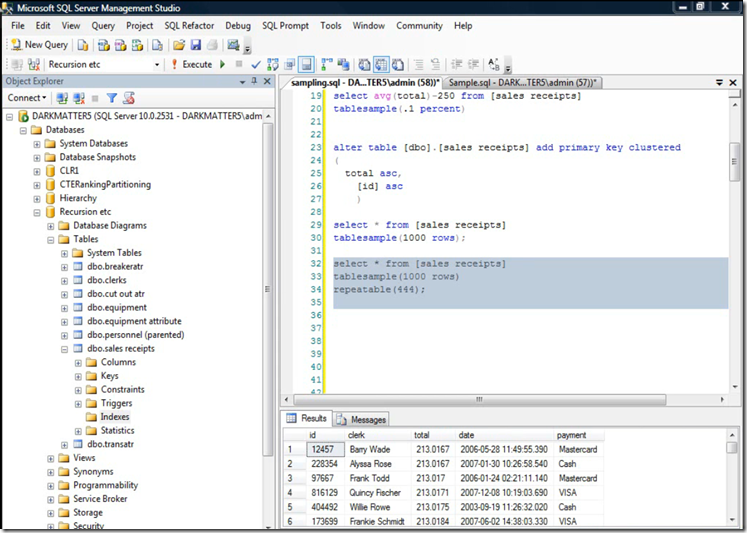
Table Sample Example
Table sample technique is using Paging(Physical storage) of SQL server to pick the rows.
TABLESAMPLE SYSTEM returns an approximate percentage of rows and generates a random value for each physical 8-KB page in the table. Based on the random value for a page and the percentage specified in the query, a page is either included in the sample or excluded. Each page that is included returns all rows in the sample result set. For example, if you specify TABLESAMPLE SYSTEM 10 PERCENT, SQL Server returns all the rows on approximately 10 percent of the specified data pages of the table.
If the rows are evenly distributed on the pages of the table, and if there is a sufficient number of pages in the table, the number of rows returned should approximate the sample size that is requested. However, because the random value that is generated for each page is independent of the values that are generated for any other page, a larger, or smaller, percentage of pages than have been requested might be returned. The TOP(n) operator can be used to limit the number of rows to a specified maximum.
When a number of rows is specified, instead of a percentage based on the total number of rows in the table, that number is converted into a percentage of the rows and, therefore, pages that should be returned. The TABLESAMPLE operation is then performed with that computed percentage.
If the table is made up of a single page, either all rows on the page are returned or none of the rows are returned. In this case, TABLESAMPLE SYSTEM can only return 100 percent or 0 percent of the rows on a page, regardless of the number of rows on the page.
Using TABLESAMPLE SYSTEM for a specific table limits the execution plan to use a table scan (a scan of the heap, or of the clustered index if one exists) on that table. Although the plan shows a table scan is performed, only those pages that are included in the result set are actually required to be read from the data file.
Blogger Labels: Server,Fundamentals,Introduction,Management,Studio,Delete,SQLCMD,Command,SQLPS,POWER,SHELL,Meta,Data,Example,Objects,LINQ,Analysis,Services,Multi,Dimensional,Expressions,Group,Same,Temporary,Table,concepts,Query,Demo,Batch,Functions,Number,rankings,employees,RANK,DENSE,NTile,indexes,Here,Hierarchies,Basic,Properties,Hierarchy,Representation,Find,Descendants,IsDescendantsOf,Nodes,Tree,Node,Depth,Search,algorithm,graph,Breadth,theory,strategy,Recursion,Tabular,Pivot,UnPivot,Cross,option,Note,operator,SELECT,clause,Also,column,Initial,Stage,Attribute,Random,selection,CHECKSUM,arguments,columns,index,Sample,technique,Physical,storage,TABLESAMPLE,SYSTEM,percentage,PERCENT,size,execution,Although,neighbor




















































































































No comments:
Post a Comment